How to operate a drone? It’s a question sparking curiosity in many, from hobbyists captivated by aerial photography to professionals exploring diverse applications. This guide unravels the intricacies of drone operation, transforming the seemingly complex into a manageable and enjoyable experience. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and safety regulations, ensuring you’re equipped to take flight confidently and responsibly.
Understanding the mechanics, mastering the controls, and adhering to safety protocols are crucial for successful drone operation. This guide provides a structured approach, breaking down each stage into easily digestible steps. Whether you’re a complete novice or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will serve as your reliable companion in the exciting world of drone piloting.
Drone Parts and Components
Understanding the individual components of a drone is crucial for safe and effective operation. Each part plays a vital role in the drone’s flight capabilities and overall performance. A malfunction in any one component can significantly impact the drone’s ability to fly, potentially leading to accidents. This section details the major components, their functions, and potential issues.
Drone Component Breakdown
| Component Name | Function | Importance | Potential Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Propellers | Generate thrust and control direction. | Essential for flight; determines speed and maneuverability. | Damage, imbalance, wear and tear leading to reduced efficiency or failure. |
| Motors | Spin the propellers; convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. | Directly responsible for propulsion; motor failure can cause a crash. | Overheating, burnout, malfunction due to voltage spikes or water damage. |
| Flight Controller | The “brain” of the drone; processes sensor data and controls motors. | Essential for stability and control; failure results in loss of control. | Software glitches, sensor malfunctions, physical damage. |
| Battery | Provides power to the drone and its components. | Without power, the drone cannot operate; determines flight time. | Low charge, damage, overheating, swelling, potential fire hazard. |
| GPS Module (if equipped) | Provides location data for autonomous flight and features like Return-to-Home (RTH). | Essential for precise positioning and safe autonomous operation. | Signal loss, interference, inaccurate positioning data. |
| Camera (if equipped) | Captures photos and videos. | Provides aerial perspective; quality depends on sensor and lens. | Lens smudging, malfunctioning image sensor, poor video stabilization. |
| Remote Controller (Transmitter) | Allows the pilot to control the drone. | The interface between the pilot and the drone; critical for safe operation. | Low battery, range limitations, connection issues, physical damage. |
Drone Battery Types
Different battery types offer varying performance characteristics. Choosing the right battery is crucial for optimal flight time and safety.
- LiPo (Lithium Polymer): High power density, lightweight, but require careful handling due to flammability. Common in hobbyist drones.
- LiFePO4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate): Higher safety rating than LiPo, longer lifespan, but lower energy density resulting in shorter flight times. Often preferred for professional applications.
Propeller Size and Flight Performance
Propeller size directly affects thrust, speed, and flight characteristics. Larger propellers generally produce more thrust but may reduce maneuverability. Smaller propellers offer better agility but may compromise lifting capacity.
Pre-Flight Checks and Procedures: How To Operate A Drone
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. Neglecting these checks can lead to accidents or equipment damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
- Inspect the drone for any physical damage (propellers, motors, body).
- Check battery charge level and ensure it’s properly connected.
- Verify the GPS signal is strong and accurate (if applicable).
- Calibrate the drone’s IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) and compass.
- Check the remote controller’s battery level and connection to the drone.
- Review local airspace regulations and restrictions.
- Ensure the flight area is clear of obstacles and people.
- Have a backup plan in case of unexpected issues (e.g., battery failure).
Sensor Calibration
Calibrating the drone’s sensors, particularly the IMU and compass, is crucial for accurate flight control and stability. Improper calibration can lead to erratic flight behavior and potential crashes. The specific calibration procedures vary depending on the drone model, so always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Powering Up and Connecting
The process of powering up and connecting to the drone varies depending on the specific model. Generally, you’ll start by powering on the drone’s battery, followed by the remote controller. The drone should then automatically connect to the controller via Wi-Fi or other wireless protocols. Always refer to your drone’s manual for detailed instructions.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding basic flight controls is the foundation for safe and competent drone operation. Mastering these maneuvers will allow you to confidently navigate your drone in various environments.
Drone Controller Functions

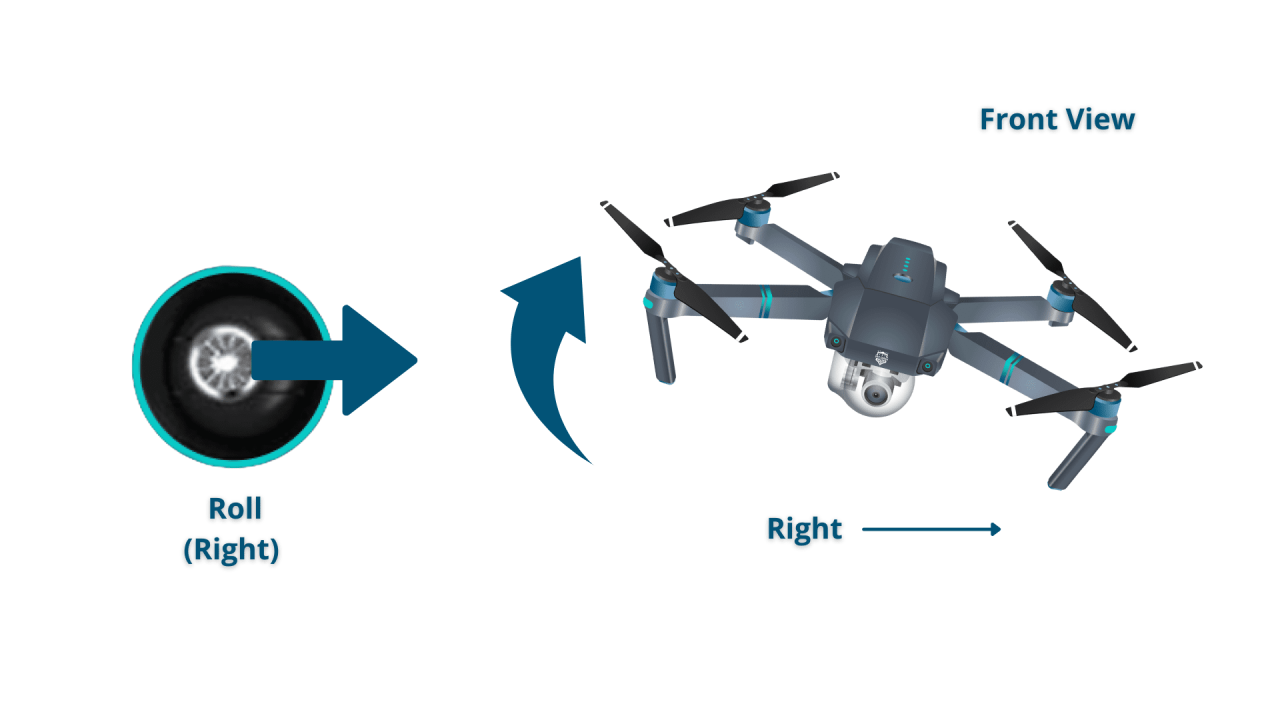
Standard drone controllers typically have two control sticks. The left stick controls altitude and yaw (rotation around the vertical axis), while the right stick controls roll (rotation around the longitudinal axis) and pitch (rotation around the lateral axis).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
- Takeoff: Gently push the left stick upwards to initiate ascent.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable altitude by keeping the left stick centered.
- Landing: Gently push the left stick downwards to initiate descent.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Push the right stick forward or backward.
- Moving Left/Right: Push the right stick left or right.
Maintaining Stable Flight
Smooth and precise control stick movements are key to maintaining stable flight. Avoid jerky movements and gradually adjust your inputs. Practice in a safe, open area to build your skills and confidence. Be mindful of wind conditions, as they can significantly affect flight stability.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Once you’ve mastered basic flight, you can explore more advanced maneuvers and autonomous flight capabilities. These techniques require practice and a thorough understanding of drone dynamics.
Drone Flight Dynamics

Drone flight is governed by principles of aerodynamics, including lift, drag, thrust, and torque. Understanding these principles is crucial for performing advanced maneuvers safely and effectively. Factors like air density, wind speed, and propeller efficiency all play a role in drone flight dynamics.
Advanced Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips, rolls, and precise positioning, require skillful control and often utilize the drone’s built-in flight modes. These modes automate certain aspects of flight, allowing for more complex maneuvers. Always practice these maneuvers in a safe, controlled environment.
GPS and Autonomous Flight
GPS and other positioning systems enable autonomous flight features like Return-to-Home (RTH), waypoint navigation, and automated flight paths. These features enhance safety and efficiency, particularly in complex environments. However, it’s crucial to understand the limitations of GPS and to always maintain situational awareness.
Drone Safety and Regulations
Drone operation involves inherent risks, and adhering to safety regulations is paramount. Understanding and respecting these regulations is crucial for preventing accidents and ensuring responsible drone use.
Potential Hazards and Preventative Measures
- Collisions: Maintain visual line of sight, avoid crowded areas, and be aware of obstacles.
- Battery Fires: Use appropriate charging methods, store batteries safely, and never overcharge.
- Loss of Control: Regularly calibrate sensors, practice in safe areas, and have a backup plan.
- Privacy Violations: Respect people’s privacy and avoid flying over private property without permission.
Safety Regulations and Guidelines
Drone regulations vary by country and region. It is crucial to research and comply with all applicable laws and guidelines before operating a drone. These regulations often cover aspects like registration, airspace restrictions, and operational limitations.
Airspace Restrictions and Permits
Many areas have restricted airspace, such as airports, military bases, and national parks. Flying in restricted airspace is illegal and can result in serious consequences. Obtaining necessary permits for specific operations may also be required.
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photos and videos. Understanding camera settings and techniques can significantly improve the quality of your footage.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Media
Factors influencing image quality include lighting, composition, and camera settings. Experiment with different angles, perspectives, and flight paths to capture dynamic and engaging content. Smooth, controlled movements are essential for avoiding shaky footage.
Camera Settings and Image Quality
Different camera settings, such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture, affect image brightness, sharpness, and depth of field. Understanding these settings and how they interact is crucial for optimizing image quality in various lighting conditions.
Setting Up and Using a Drone Camera, How to operate a drone
- Familiarize yourself with your drone’s camera controls and settings.
- Adjust camera settings based on lighting conditions and desired image quality.
- Compose your shots carefully, considering angles, perspectives, and background elements.
- Practice smooth and controlled flight movements to minimize camera shake.
- Review your footage and adjust settings as needed.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are essential for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and preventing unexpected issues during flight.
Routine Maintenance Schedule
- Inspect propellers for damage and replace as needed.
- Check motor mounts for tightness and secureness.
- Clean the drone body and propellers after each flight.
- Store the drone and battery in a cool, dry place.
- Perform a full system check before each flight.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Common issues include battery problems (low charge, swelling), motor failures (overheating, burnout), and connectivity problems (signal interference, low battery in the controller). Refer to your drone’s manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Cleaning and Storage
Proper cleaning and storage are crucial for maintaining the drone’s functionality and preventing damage. Use a soft cloth to gently wipe down the drone body and propellers. Store the drone in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Always store batteries separately, following manufacturer recommendations.
Types of Drones and Their Applications
The world of drones is diverse, with various types catering to different needs and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right drone for your specific purpose.
Drone Types and Capabilities
| Drone Type | Size | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Consumer Drones | Small to medium | Camera, GPS, obstacle avoidance | Photography, videography, recreational flying |
| Professional Drones | Medium to large | High-quality camera, advanced sensors, long flight time | Mapping, surveying, inspection, delivery |
| Industrial Drones | Variable | Heavy-lifting capacity, specialized sensors, rugged design | Construction, agriculture, search and rescue |
Drone Applications in Various Industries
Drones are revolutionizing various industries, offering efficient and cost-effective solutions. In agriculture, drones are used for crop monitoring and precision spraying. In construction, they aid in site surveying and progress tracking. Delivery services utilize drones for faster and more efficient package delivery.
Drones in Search and Rescue
Drones play a vital role in search and rescue operations, providing aerial surveillance and assisting in locating missing persons or victims of natural disasters. Their ability to access difficult terrain and provide real-time imagery is invaluable in these critical situations.
Successfully operating a drone involves a blend of technical understanding, practical skill, and responsible decision-making. From understanding your drone’s components and performing thorough pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls and adhering to safety regulations, each step contributes to a safe and rewarding experience. By following the guidelines presented in this guide, you’ll not only gain the confidence to fly but also appreciate the immense potential of drone technology, whether for recreational purposes or professional applications.
Remember, continuous learning and practice are key to honing your skills and maximizing your drone’s capabilities.
Question Bank
What is the legal age to operate a drone?
Legal age restrictions vary by location and drone type. Check your local regulations.
How far can I fly my drone?
Distance limitations depend on your drone model, battery life, and local regulations. Always stay within visual line of sight.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and safety protocols. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which provides comprehensive tutorials. From there, you can practice your skills and progress to more advanced drone maneuvers, always prioritizing safe flight operations.
Most drones have a return-to-home (RTH) function. If not, attempt to regain connection; otherwise, the drone will likely land where it is.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibration frequency depends on usage. It’s generally recommended before each flight, or if you notice erratic behavior.
What type of insurance is needed for drone operation?
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. A crucial aspect is learning the proper control techniques, and for a comprehensive guide, you might find this resource helpful: how to operate a drone. This will help you confidently handle your drone and ensure safe and successful flights. Ultimately, safe and responsible operation is paramount when learning how to operate a drone.
Insurance requirements vary by location and use case. Liability insurance is often recommended.
